Introduction
Think about a vigorous market the place various individuals commerce issues and companies, counting on belief and openness. The important thing problem is to safe the integrity of transactions with out counting on intermediaries.
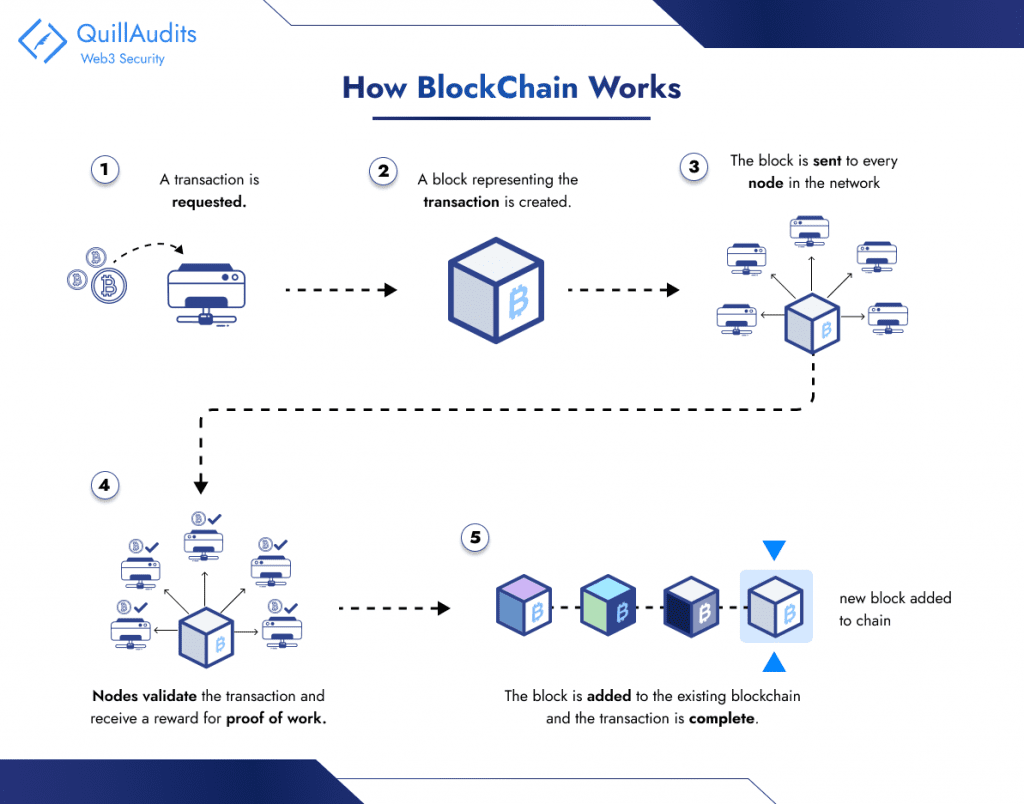
That is the place blockchain comes into play, serving as a cutting-edge database system that permits open sharing of knowledge inside a enterprise community. The data is saved in related blocks. Any modifications to the chain require approval from the entire community to take care of order.
This technique ensures a protected and unchangeable file for monitoring transactions, orders, and accounts. It has built-in measures to forestall unauthorized actions, guaranteeing a dependable and reliable transaction historical past.
Conventional databases face challenges in precisely recording monetary transactions, particularly in eventualities like property gross sales. Individuals can observe cash exchanges, however belief points can come up if both celebration disagrees with the transaction. To forestall authorized problems, a dependable third celebration should oversee and authenticate transactions, introducing complexity and a single vulnerability level.
Blockchain addresses these considerations by establishing a decentralized, tamper-resistant transaction recording system. In a property sale, as an illustration, separate ledgers are created for the customer and vendor.
Transactions require approval from each events and are immediately up to date of their respective ledgers. Any tampering with historic transactions impacts the complete ledger. These blockchain options have pushed its adoption in varied sectors, together with the event of digital currencies like Bitcoin.
Bitcoin, launched in 2009, wasn’t simply the primary cryptocurrency; it additionally birthed the revolutionary expertise behind it – the blockchain. This digital ledger has modified industries by securely recording data in a clear and tamper-proof manner.
Earlier than Bitcoin, digital currencies struggled with the double-spending drawback, the place a single digital unit could possibly be used a number of instances. The Nakamoto Consensus, named after Bitcoin’s pseudonymous creator, launched a algorithm to sort out this difficulty.
Central to those guidelines is the proof-of-work (PoW) algorithm, which requires members to unravel complicated issues, making it expensive and deterring malicious actions. This algorithm is employed inside a Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) peer-to-peer community, enhancing the community’s resilience towards failures or assaults.
In a decentralized system like Bitcoin, a number of computer systems (miners) must agree on the validity of transactions and the state of the blockchain. That is the place the consensus mechanism is available in. Bitcoin’s PoW system requires miners to unravel complicated mathematical puzzles to earn the suitable so as to add a block to the blockchain. This computationally intensive course of secures the community towards malicious actors making an attempt to govern transactions.
Understanding the Downside: The Byzantine Generals Downside
Think about a battlefield surrounding the Byzantine Empire’s capital. A number of Byzantine generals, every commanding their very own military, should coordinate their assault on the town to succeed. Victory hinges on unanimous settlement: all generals should assault concurrently, or the defenders will defeat them one after the other.
Nevertheless, there’s a twist:
Treacherous generals: Some generals is likely to be traitors, working for the enemy or with their very own agendas. They will ship deceptive messages or just refuse to cooperate.
Unreliable communication: Messengers carrying orders may be intercepted, delayed, and even impersonated. The generals can’t make certain of the data they obtain.
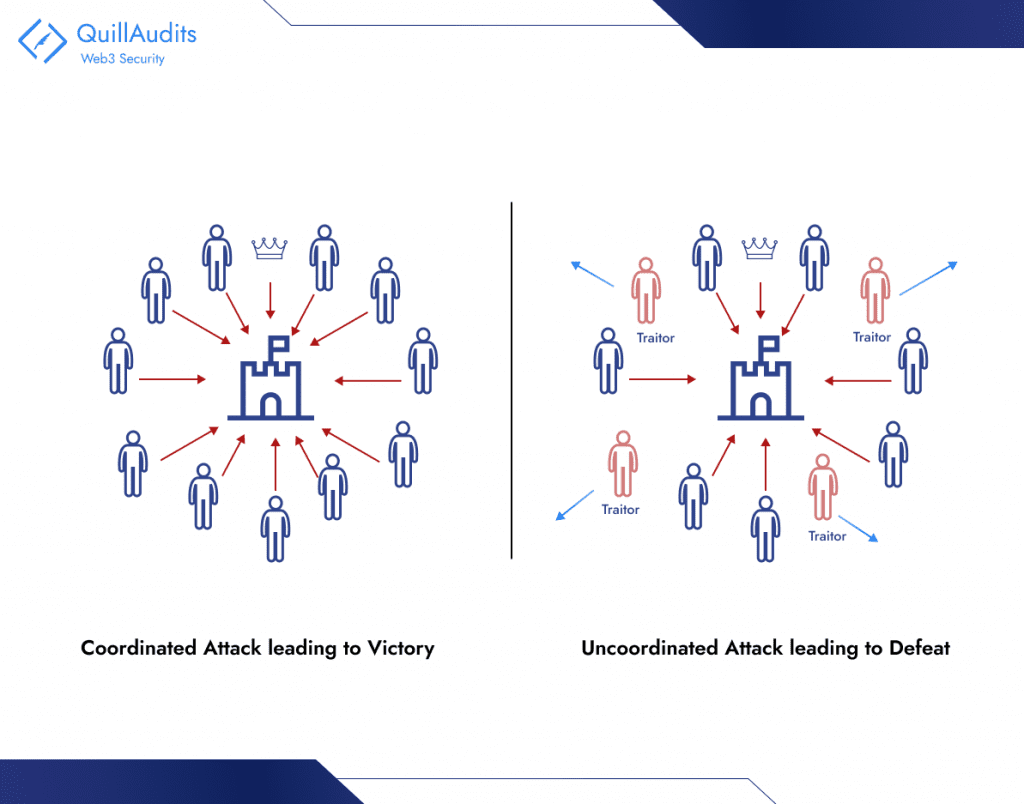


That is the essence of the Byzantine Basic’s Downside: reaching consensus in a decentralized system the place belief is unsure. It’s a vital problem for distributed networks like blockchains, the place impartial nodes should agree on the state of the community (e.g., transaction validity) with out counting on a government.
Challenges in a Trustless Surroundings
- Malicious Actors: Byzantine nodes can deliberately disrupt the community by Sending conflicting messages, Complicated different nodes, and hindering consensus.
- Denying service: Refusing to take part within the consensus course of. Fabricating knowledge: Creating false data to govern the community.
- Unreliable Communication: Technical points can result in Message delays, Transactions or blocks taking longer to propagate, probably inflicting inconsistencies.
- Message loss: Info will get misplaced in transit, creating gaps within the community’s data.
- Reaching Settlement: Even with sincere nodes, attaining consensus effectively may be troublesome, particularly with a lot of members. Totally different consensus algorithms provide various trade-offs between pace, safety, and fault tolerance.
Nakamoto Consensus: A Answer to the Byzantine Generals Issues
Within the Byzantine Generals Downside, reaching a standard determination, like in blockchain, is significant. That is much like the Nakamoto consensus in blockchain, a key a part of Bitcoin.
The blockchain acts as a public file, like a ledger, exhibiting all Bitcoin transactions. That is essential for Bitcoin consensus guidelines. When all Bitcoin community customers, or nodes, agree on transaction particulars and their sequence, they affirm possession and allow a reliable, decentralized cash system, avoiding central management. That is what bitcoin consensus is about.
Blockchain’s decentralized nature relies upon enormously on consensus strategies, just like the Nakamoto consensus on permissionless and anonymous techniques, to validate transactions. It’s a community the place customers can see all the pieces transparently, fostering belief. Its shared ledger distinguishes it from different strategies.
Understanding and analyzing Nakamoto consensus reveals its potential for any system requiring correct verification. This describes the Nakamoto consensus based mostly on permissionless and anonymous rules, a cornerstone in blockchain expertise.
1. Proof-of-Work (PoW): Fixing Puzzles for Energy
Think about miners competing to unravel complicated mathematical puzzles. The primary to discover a answer will get so as to add a block to the blockchain, a publicly viewable ledger of transactions. However fixing these puzzles takes actual computational energy and power, performing as a “price operate” to discourage unhealthy actors. Miners are incentivized to be sincere, as fraudulent blocks face rejection by the community.
2. Blockchain and Hashing: Constructing a Chain of Belief
Consider the blockchain as a sequence of interlocking blocks. Every block accommodates knowledge (transactions) and a singular cryptographic fingerprint known as a hash. This hash is created by chaining collectively the earlier block’s hash and the brand new knowledge. Altering any knowledge inside a block invalidates its hash and all subsequent hashes, making tampering just about unimaginable.
3. Longest Chain Rule: May Makes Proper (Nearly)
Now, think about a number of miners discovering options and creating blocks concurrently. The community adopts the longest chain precept, accepting the chain with essentially the most collected PoW because the true model of the blockchain. This incentivizes miners to construct upon the present chain, relatively than beginning their very own, solidifying consensus.
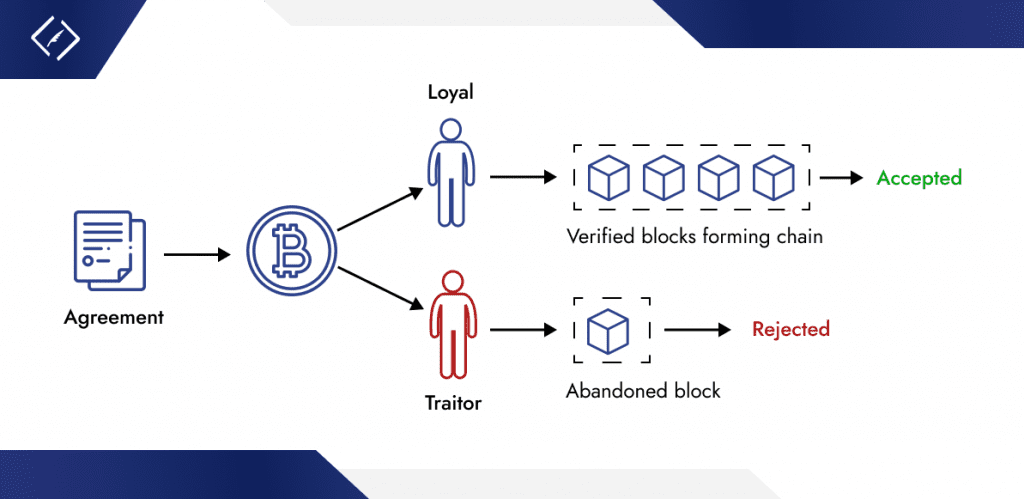


Illustration of Consensus and Prevention of Double-Spending:
- Miners compete to unravel mathematical puzzles by PoW, guaranteeing that solely legitimate blocks are added to the blockchain.
- Every block is securely linked to its predecessor through cryptographic hashing, making any alteration of previous transactions simply detectable.
- The longest chain rule ensures that the blockchain model accepted by the bulk is at all times thought of the professional one.
This framework collectively secures the blockchain, facilitates consensus amongst members, and successfully prevents double-spending. Double-spending is averted as a result of as soon as a transaction is confirmed in a block, altering it might require re-mining that block and all subsequent blocks at a quicker charge than the remainder of the community, which is virtually infeasible because of the PoW mechanism.
Advantages of Nakamoto Consensus
Decentralization: The energy of blockchain is derived from Nakamoto Consensus, which distributes energy amongst quite a few nodes to fend off censorship and remove single factors of failure. With simply an web connection wanted for worldwide, unrestricted participation, this decentralized system promotes monetary inclusion with out regard to location.
Trustlessness: Blockchain expertise reduces reliance on outdoors events to validate transactions, permitting for an automatic, self-governing system that provides customers direct management over their knowledge and belongings, selling autonomy and minimizing bias.
Safety: Byzantine Fault Tolerance and Proof-of-Work, two sturdy cryptographic foundations constructed into the blockchain, assure tamper-proof data and system resilience towards interruptions. Incentives based mostly on recreation principle assist miners higher align their efforts with community safety and stability.
Transparency: Blockchain ensures public, verifiable transactions and an immutable historical past, enhancing belief, accountability, and market effectivity by clear, unalterable data.
Criticisms and Potential Options
Nakamoto Consensus, the engine behind blockchains like Bitcoin, has modified finance and tech, but it has flaws. Utilizing Proof of Work (PoW), it calls for big power, elevating sustainability points. PoW additionally limits scalability, inflicting sluggish transactions and excessive charges and hindering widespread adoption. Recognizing these issues is significant for advancing decentralized techniques.
Luckily, the blockchain ecosystem is brimming with innovation. To beat the drawbacks of PoW, researchers and builders are exploring different consensus mechanisms, with Proof of Stake (PoS) gaining vital traction. In PoS, validators are chosen based mostly on their stake within the community’s cryptocurrency, eliminating the necessity for energy-intensive mining. This not solely reduces power consumption but in addition probably will increase transaction speeds and scalability.
Conclusion
The Nakamoto Consensus is essential to Bitcoin’s success. It’s a novel technique that solves the Byzantine Generals Downside, guaranteeing safe and decentralized digital transactions. That is achieved by combining Byzantine Fault Tolerance with Proof-of-Work, making a community that protects towards fraud and maintains transaction integrity. Nevertheless, there’s debate over its sustainability and power use. This has led to exploring alternate options like Proof of Stake for extra scalable blockchain options. It’s important for everybody, from lovers to skeptics, to grasp and focus on these applied sciences. They’re shaping the way forward for decentralized techniques and may result in a extra environment friendly, inclusive world. The evolution of Bitcoin and blockchain is an unfolding story, open for all to contribute to.
3 Views

