Particular because of Sacha Yves Saint-Leger & Danny Ryan for assessment.
On this installment, we’ll talk about the consensus mechanisms behind eth2. Eth2 has a novel strategy to deciding which block is the top of the chain, together with which blocks are and will not be part of the chain.
Through the use of a hybrid between the 2 mechanisms, eth2 goals to have a consensus which, along with being fast and protected when the community is behaving usually, stays protected even when it’s being attacked.
A Trilemma
FLP impossibility is a core consequence within the discipline of distributed computation which states that in a distributed system it isn’t potential to concurrently have security, liveness, and full asynchrony except some unreasonable assumptions might be made about your system.
Security is the concept choices can’t be unmade whereas liveness captures the notion that new issues might be determined. A protocol is asynchronus if there isn’t any certain on how lengthy a message might take to get delivered.
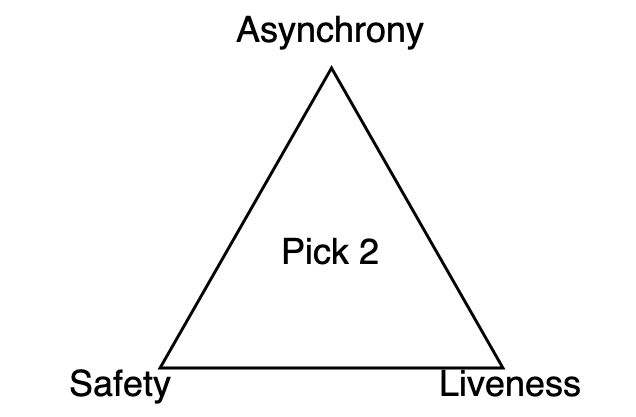
If nodes may talk reliably, at all times comply with the protocol actually and by no means crash, then consensus could be simple, however that isn’t how the world works. When these assumption do not maintain, FLP Impossibility is the proof that at the least certainly one of: security, liveness, or full asynchrony have to be compromised.
GHOSTs and their opinions on forks
Eth2 makes use of Grasping Heaviest Noticed Subtree (GHOST) as its fork-choice rule. GHOST selects the top of the chain by selecting the fork which has essentially the most votes (it does this by contemplating all the votes for every fork block and their respective little one blocks).
Put one other approach, every time there’s a fork, GHOST chooses the facet the place extra of the most recent messages help that block’s subtree (i.e. extra of the most recent messages help both that block or certainly one of its descendants). The algorithm does this till it reaches a block with no kids.
GHOST has the good thing about lowering the efficacy of assaults throughout occasions of excessive community latency in addition to minimizing the depth of chain reorgs when in comparison with the longest-chain rule. It’s because whereas an attacker can maintain constructing blocks effectively on their very own chain thereby making it the longest, GHOST would select the opposite fork as there are extra votes for it in whole.
Particularly, eth2 makes use of a variation of GHOST which has been tailored to a PoS context known as Newest Message Pushed GHOST (LMD-GHOST). The thought behind LMD-GHOST is that when calculating the top of the chain, one solely considers the newest vote made by every validator, and never any of the votes made previously. This dramatically decreases the computation required when working GHOST, for the reason that variety of forks that have to be thought-about to execute the fork alternative can’t be larger than the variety of validators ( in Large O notation).
Below the principles of GHOST, validators/miners can at all times attempt to add a brand new block to the blockchain (liveness), they usually can do that at any level within the chain’s historical past (asynchronous). Since it’s reside and absolutely asynchronous, because of our pal FLP, we all know it may’t be protected.
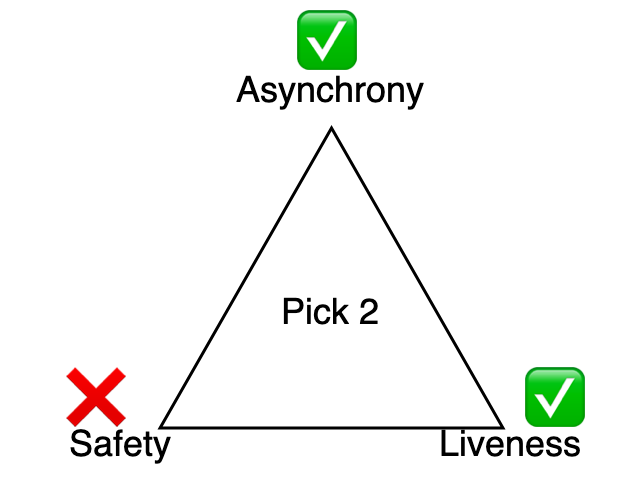
The dearth of security presents itself within the type of reorgs the place a sequence can out of the blue swap between forks of arbitrary depth. Clearly that is undesirable and eth1 offers with this by having customers make assumptions about how lengthy miners’ blocks will take to be communicated with the remainder of the community, this takes the type of ready for confirmations. Eth2, against this, makes no such assumptions.
The pleasant finality gadget
A blockchain with none notion of security is ineffective as a result of no choices may very well be reached and customers couldn’t agree on the state of the chain. Enter Casper the Pleasant Finality Gadget (Casper FFG). Casper FFG is a mechanism which favours security over liveness when making choices. Which means that whereas the choices it makes are closing, underneath poor community circumstances, it could not be capable of resolve on something.
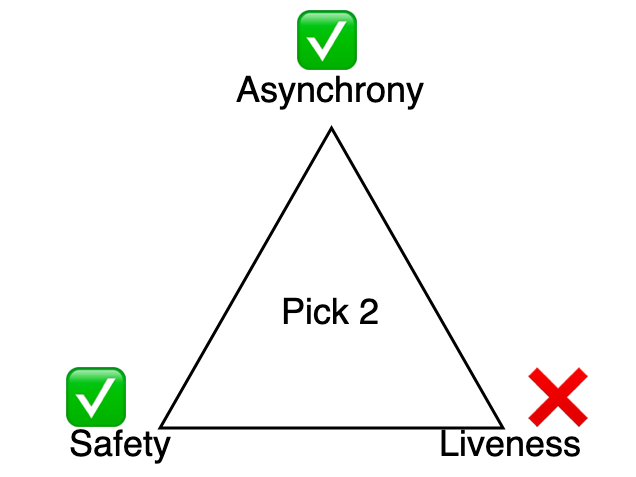
FFG is a crypto-economic adaption of the traditional Sensible Byzantine Fault Tolerent (PBFT) which has phases the place nodes first point out that they’d wish to agree on one thing (justification) after which agree that they’ve seen one another agreeing (finalisation).
Eth2 doesn’t attempt to justify and finalise each slot (the time when a block is predicted to be produced), however as an alternative solely each 32 slots. Collectively, 32 slots is known as an epoch. First, validators signal that they agree with all 32 blocks in an epoch. Then, if achieve this, the block is justified. In a later epoch, validators get one other likelihood to vote to point that they’ve seen the sooner justified epoch and if do that, the epoch is finalised and is eternally part of the eth2 chain.
FFG employs a intelligent trick. Votes really encompass two sub-votes, one for the epoch that’s making an attempt to be justified and one other for an earlier epoch that’s to turn out to be finalised. This protects lots of additional communication between nodes and helps to attain the purpose of scaling to hundreds of thousands of validators.
Two ghosts in a trench coat
Consensus inside eth2 depends on each LMD-GHOST – which provides new blocks and decides what the top of the chain is – and Casper FFG which makes the ultimate determination on which blocks are and will not be part of the chain. GHOST’s beneficial liveness properties enable new blocks to rapidly and effectively be added to the chain, whereas FFG follows behind to supply security by finalising epochs.
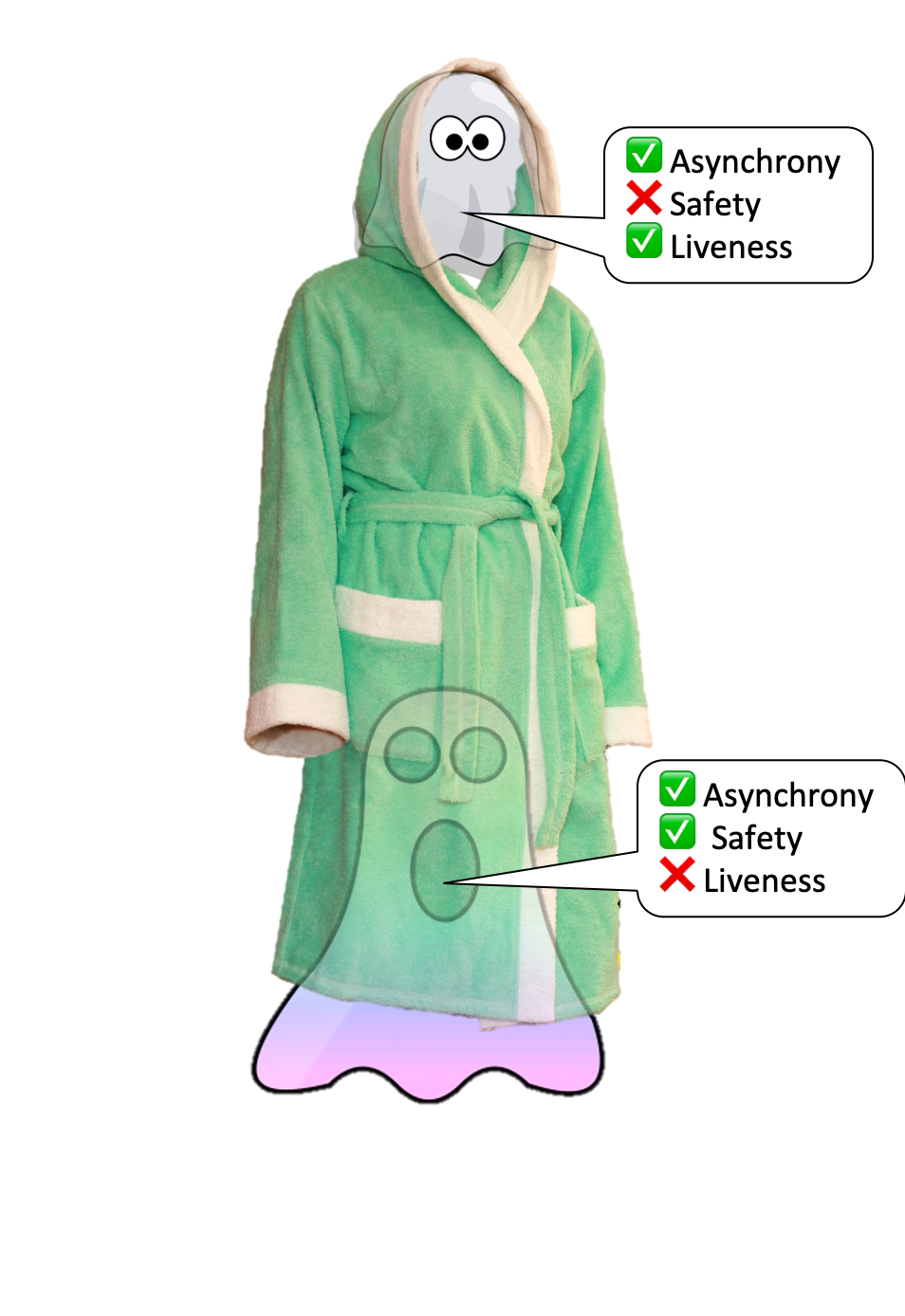
The 2 protocols are merged by working GHOST from the final finalised block as determined upon by FFG. By building, the final finalised block is at all times part of the chain which implies GHOST would not want to contemplate earlier blocks.
Within the regular case when blocks are being produced and validators are voting on them, these blocks are added to the top of the chain by GHOST, and never lengthy after justified and finalised by FFG (which considers the previous few epochs).
If there may be an assault on the community and/or a big proportion of validators go offline, then GHOST continues including new blocks. Nonetheless, since GHOST is reside, however not protected, it could change its thoughts concerning the head of the chain – it is because new blocks are regularly added to the chain, which implies nodes continue learning new data. FFG alternatively, favours security over liveness that means that it stops finalising blocks till the community is steady sufficient for validators to vote constantly once more.

