Half I
Typically Ethereum is in comparison with a singleton Digital Machine. Whereas that is right in some sense; I feel it is a little more. To start with what’s a singleton in a distributed system? It’s merely a set of values that some threshold of contributors have come to consensus on. A Digital Machine is a computational atmosphere that’s remoted from the bodily pc and from different environments.
A hypervisor permits the bodily machine to be multiplexed into many VMs. In accordance with this definition a standard hypervisor is the net browser the place webpages are VMs. One other instance of a hypervisor can be Ethereum as every contract will get its personal remoted computational atmosphere.
There are lots of variations between the frequent net browser and Ethereum, however one of many extra attention-grabbing ones is how VMs talk and work together with one another. Net browsers don’t present a manner for VMs to instantly work together whereas Ethereum however gives some easy mechanism for VM interplay; the opcodes CALL, DELEGATECALL, CALLCODE, CREATE. On this publish will discover the query; What different guidelines might exist? Can we generalize VM interactions and offered an summary framework for these interactions? And from this framework can we purpose about distributed hypervisors?
Most of this publish will resemble ambient calculus however there are a number of notable variations from ambient calculus and what’s introduced right here. The diagrams might be regarded as bigraphs however they need to even be self explanatory. Half I’ll describe the principles of ambients after which apply them to Ethereum. Half II will focus on scaling within the phrases of ambients as laid out by half I.
What’s an Ambient?
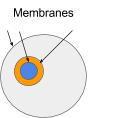
An ambient is a bounded place during which computation can happen. A boundary determines what’s inside and what’s outdoors an ambient. For ambients we name this boundary a membrane. The realm inside an ambient is hierarchical namespace. Objects can exist inside an ambient. The objects are addressable by way of the namespace. There are three base parts in ambient calculus. Objects, Namespaces and Messages.
Hierarchical Namespaces
Some of the acquainted namespace is the file system tree. Namespaces enable us to establish objects with paths or names. Namespaces right here have the next properties
- For each doable path there exists a null or an object
- At any level within the namespace you’ll be able to transfer up or down. That is what’s implied by hierarchical.
- Each path has a root related to it. The basis uniquely identifies the content material for all of the paths under the basis. You may consider the basis as a pointer to the content material of the trail.
- Paths might be learn from or written to
- Messages might be despatched alongside paths to things
Object Varieties
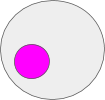
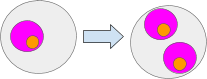
What’s an object? It’s only a worth. In actual life computing its just a few knowledge. This knowledge might be interpreted in a number of alternative ways. Any Object might be learn as knowledge. The pink circle is a few knowledge that exists within the gray ambient.
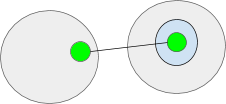
Objects can be interpreted as ambients. This enables ambients to have sub-ambients. Right here the orange and gray circles are ambients.
Objects can be interpreted as ports. Two or extra ports kind a I/O channel. Channels enable messages to be despatched to ambients in a unique namespaces. Channels might be regarded as tunnels by an ambient’s membrane. Each the doorway and exit ports should exist someplace in a namespace. Right here the inexperienced objects symbolize ports.
Lastly messages can be thought of to be an object. Messages are particular since they’re outlined as objects in movement or regarded as objects with velocity.
To Recap; Objects might be the next sorts
Objects :: =
Information
Port
Ambient
Message
Messages
As said above messages are objects which are in transit. Messages might be despatched by a namespace and thru channels. Messages have the next properties which are set by the techniques message handler. They don’t seem to be all intrinsically a part of the message however as you will note later they make working with messages simpler.
- To – The trail to the vacation spot of the message. That is immutable.
- From – The sender of the message. That is immutable.
- Kind – The kind of message. That is immutable.
- Information – The message’s physique. That is immutable.
- Heading – The vacation spot relative to its present place. If `Heading` is `null` then the message has arrived at its vacation spot and can journey no additional. This isn’t instantly encoded within the message however as a substitute set by the techniques message handler. That is mutable.
- Route – Which route the message is touring. It will probably both be going ‘out’ of the ambient or going ‘in’ to the ambient. That is mutable.
Message Varieties
Message have the next sorts which have corresponding instructions used to ship them.
Set(path, worth) - Units a path to a given worth
Get(path) - Will get a price of the given path
SetRoot(path, root) - units the basis of `path` to `root`
GetRoot(path) - Will get the trail’s root
Name(path, knowledge) - Sends a message alongside the given path
Join(to, from, choices) - creates a channel between two paths.
Deleting
It may not be instantly apparent the way to delete an ambient or different objects. To do that we use the `Set` and `SetRoot` message.
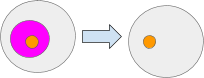
The Set message units the worth of a path. Setting a path to null is equal to deleting the contents of that path. For instance Set(‘pinkAmbient’, null) Right here the pink ambient is about to null. Be aware the the orange ambient was not deleted.
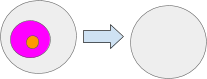
The SetRoot message units the basis of a path. If the basis is about to null all the trail values under the basis will turn out to be null. For instance CopyRoot(‘pinkAmbient’, null) will set the pink ambient’s root to null which will even trigger the orange ambient be to null.
After all if we did one thing like SetRoot(‘a’, ‘pinkAmbientsRoot’) we’d copy the pink Ambient and all of it contents to path “a”
Iterating the by a Namespace.
In lots of instances it helpful to iterate by all of the ambients in a given namespace. A technique we might strategy that is to `get` every path within the namespace. However the issue is that the majority namespaces are infinite. A greater manner can be to offer an express iteration technique. Let’s add a message
Subsequent(path) - Given a path return the subsequent non-null path within the namespace.
This suggests that namespaces all will need to have an order. Additionally this gives us with a pleasant approach to construct extra difficult ambient operations like merging two or extra ambients. We additionally want this to construct kind checking.
Membrane computing
The ambient’s border is its membrane. It will probably filter message coming into and going out of it. For instance the if the gray ambient sends a Set(‘blueAmbient’, null) message to the trail of the ‘blueAmbient’ it would undergo the membrane of the orange ambient. The orange ambient can determined whether or not or to not let the message go by.
A Membrane API
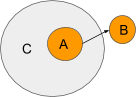
Lets stroll by a small instance of what programming ambients would possibly appear to be.
Ambient A is attempting ship a message to ambient B however the message has to undergo Ambient C. Since A is a sub-ambient of C, C can management this message. Here’s what an api for coping with messages would possibly appear to be. Let say that we’ve a operate ‘onMessage’ that will get ran each time the ambient will get a message. Here’s what C membrane might appear to be.
/** * Enable any message to go by the membrane besides messages from Ambient D * @technique onMessage * @param message - the message that's leaving the ambient * @retruns Boolean */
operate onMessage(message) {
if(Message.sender != ”A” && Message.route == ‘out’){
Message.heading = ‘D’
}
}
C filters any messages coming from the trail ‘A’ which are going out of it. As an alternative of letting the message go to its supposed location C reroutes the message to location “D”. Discover how C set the heading on the message. If C set Message.heading to null then the message would cease there. C can solely determine the place to ahead the message or to cease it.
The power of ambients to filter and determine which message can journey by them is a vital one. That is also referred to as Membrane computing. It’s going to assist you to construct versatile and simply composable contracts. Particularly in terms of administration of sub-contracts.
Mapping ambients to a Ethereum
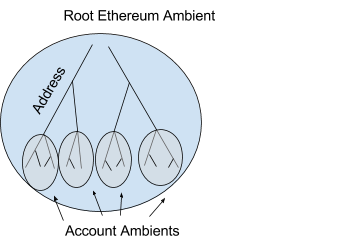
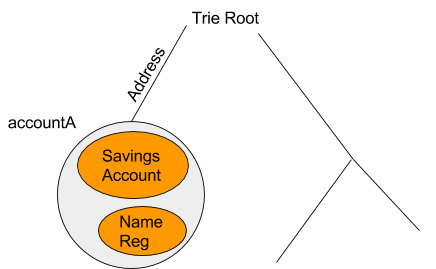
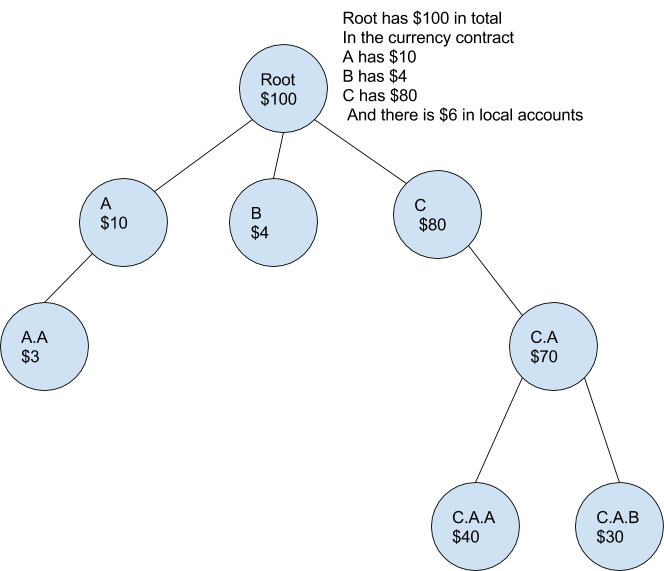
Now that we’ve the fundamentals of ambients let’s apply them to a one in all our favourite knowledge constructions, the merkle tree. To start out you might need already acknowledged the truth that a contract in Ethereum is like an ambient and the namespace is offered by the merkle tree.
Namespace ::=the merkle tree
This might be visualized like this
In Ethereum every ambient has an tackle that’s 20 bytes lengthy and appears like the next 0x1158c3c9a70e85d8358972810ed984c8e6ffcf0f. Ethereum ambients have storage that enable them retailer retailer arbitrary values completely. Storage is accessed and manipulated with the SSTORE and SLOAD opcodes. The equal to those are the set and get messages. Additionally command Name is equal.
SetRoot, GetRoot and Join do not need equivalents in Ethereum at present. SetRoot and GetRoot would learn from and manipulate the underlying mekle trie.
Now we’re going to deviate from present Ethereum to Ethereum + Ambients. Allow us to say the contract 0x1158c3c9a70e85d8358972810ed984c8e6ffcf0f units the worth ‘doge’ on the addresses ‘coin’ which is 636f696e in hex. The tackle 0x1158c3c9a70e85d8358972810ed984c8e6ffcf0f/636f696e would then comprise the worth ‘doge’. Additionally ‘doge’ may be interpreted as code if a Name was made to that path.
Private Accounts
Lets use a private Ethereum account for instance. For comfort we’re going to say the tackle of the account is “accountA” which can be represented because the gray ambient. This ambient would maintain the fundamental signature validation code as seen within the forex and crypto abstraction. If the consumer wished to position a spending limits on herself then she might create a “Financial savings Account” which might solely allow a specific amount of ether to be spent per day. Moreover the consumer might create her personal customized Title Reg or different monetary apps. The hierarchical nature of the ambients permits you to construct up administrative “zone”. They’ll make code very modular because the “saving account” and different contracts don’t have to have any code devoted to checking if the consumer is an admin or checking different credential since that might be carried out by the accountA’s ambient.
On this part we are going to discover some concepts about scalability by way of ambients.
The fundamental thought of scalability is pretty easy. Most strategies proposed up to now contain these properties:
- Separating some a part of the state right into a shard that’s processed impartial of the opposite shards
- Some form of cross validation; the place some portion of a shard’s work is checked by different shards which is often triggered by cross shard communication.
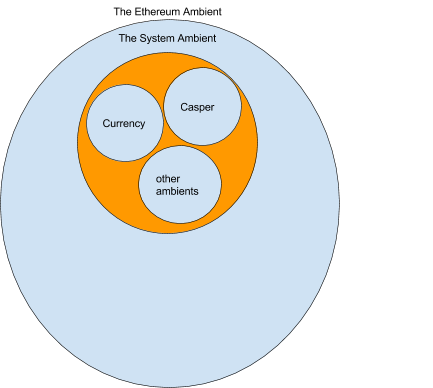
We’re additionally assuming we’ve a Proof of Stake algorithm like Casper and this algorithm is carried out in a set of ambients. Together with casper we’ve a forex ambient that tracks the quantity of ether every account ambient has. These ambients are grouped collectively into the system ambient. There possibly many extra ambients within the system ambient however for now we are going to simply take into account these.
For now we are going to merely assume that casper works and produces the right state for the “Ethereum Ambient”.
Sharding
If Ethereum is profitable, the quantity of transaction will improve over time. After some time a excessive quantity of transactions will trigger the value of fuel to extend. At a sure threshold decided by a Threshold operate the Casper ambient will produce a shard. It ought to be famous that solely from the casper ambient’s perspective is Ethereum sharded. Everybody else sees Ethereum as one continued namespace extending by many ambients.
There’s some threshold that’s wanted to create a shard in Casper. This isn’t the main focus of this publish however we will picture a number of the parameters it is perhaps based mostly off of. It might use gasPrice to transaction ratio. Or might it use a voting system or a bidding system or mixture of all them.
Moreover the Threshold operate we are going to assume the next about Casper:
- Anybody can contest a state transition.
- Validators are randomly assigned to shards. These kind a validation group that run Casper for that shard.
- Validator could also be assigned to a couple of shard
- New shards should be initially validated by all validators
- The full quantity in bond in a validation group of a shard ought to be equal to what the shard is value.
Creation of Shards
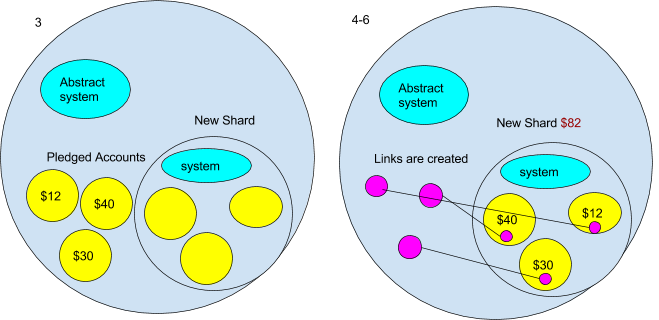
- For now we are going to assume that new shards will begin out as an empty ambient. However consider this may not at all times be the case- for instance a very efficiently dapp might maybe pay the Casper contract sufficient to make it worthwhile for the validator to create a shard out of it. However for now it’s empty.
- The very first thing that occurs to the brand new shard ambient is the system contracts are copied to it. However we don’t need an actual copy of the present system ambient. It is because it accommodates the present state. We wish an empty forex contract and an empty Casper contract, and many others. To do that the Ethereum ambient will need to have an “summary” system ambient from which we then copy. We will picture the summary system ambient would have a message handler that solely allowed messages that have been copying it. It might seems to be one thing like this:
operate onMessage(message) { // disallows messages getting any subambient // roots from the summary system if(message.kind !== `getRoot ` || message.headed !== ‘’){ message = null // kills the message } }The brand new shard would ship a `getRoot` to the summary system. Then it could use `setRoot` internally to repeat the summary system its namespace.
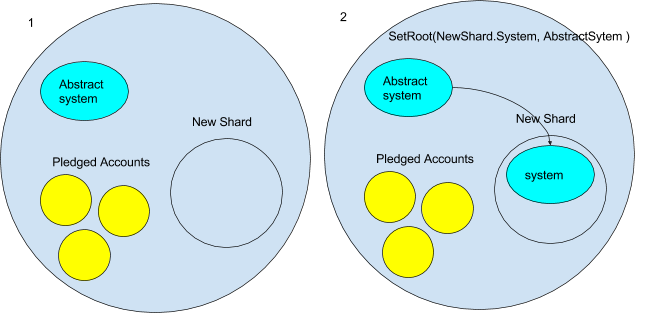
- A part of the edge operate is perhaps pledges from different ambients to maneuver to a brand new shard as soon as it’s created. When the brand new shard is created, all of the accounts that pledged to maneuver are mechanically moved to the brand new shard. That is carried out after the system ambient is in place. The accounts are additionally copied with the `CopyRoot` command.
- After they’ve been copied their authentic tackle is changed by a port (created by the “Join” command) making a channel to their new account on the brand new shard.
- The forex contract then units the quantity of ether that the shard has to the sum of the accounts that pledge to maneuver.
- Lastly the within the new shards forex, the contract is populated by the values of the copied accounts.
Fractal chains?
The top end result can be that the highest degree ambients now not “see” the person accounts which are within the new shard, as a substitute it solely see the worth of the sum of the account on the brand new shard ($82 within the diagram). Whereas the brand new shard’s forex contract retains observe of the person accounts within the shard. This resembles a fractal in the best way that a part of the entire is encoded in each part of the construction.
Additionally if anybody makes use of the previous tackle of an ambient that moved, their messages can be forwarded to them by way of the channels. There are some disadvantages to utilizing the channels; 1) its can be extra pricey 2) there can be increased latency.
Monetary Isolation – Counterfeiting Assaults
The shards might be seen forming a hierarchy; every shard ambient conserving observe of its accounts and the sum of the accounts in its youngsters shards.
This creates a powerful assure of the correctness of account balances. No shard can create counterfeit forex and ship it to a different shard. Moreover the safety is additive. That means that the extra shards {that a} message crosses the stronger the assure that it’s right. We’re assuming that each validation group will verify that transaction going by it. If a transaction goes from shard C to C.A.B then shards C, C.A and C.A.B all will verify the transaction and ask the shard C for merkle proof of the sender’s account. If the transaction was discovered to be invalid after the validator’s authorized it then the validators in all three teams would lose their deposits. If accounts have been defrauded they might first be refunded from the validators deposits.
Let’s take into account a protracted vary counterfeit assault. That is the place a validation group on a shard creates an account with an invalid quantity of forex related to it after which they simply go away it within the shard. In the event that they ever attempt to transfer it from the shard the mum or dad validation group will request a whole transaction log that reveals how the accounts obtained its cash. At this level the assault would fail until the mum or dad validation group was additionally compromised. And in a protracted vary assault the attackers wait till the mum or dad validation group is compromised. One of the simplest ways to counter that is to make every validation group chargeable for the entire historical past of its shard and to not launch the bonds to unbonded validators after a number of epochs. This provides the present validation group an incentive to verify the earlier validation teams work.
A technique during which a validation group can verify the earlier validation group work rapidly is to simply sum the transaction graph. We will consider all messages that switch forex as forming a directed graph. Since we all know the worldwide quantity of forex that the shard has, a validation group simply must sum up the entire quantity the accounts had for every block within the earlier epoch and verify it towards the identified world quantity.
To recap, a number of properties that may improve safety are:
- Give the Mother or father Validation group an incentive to verify the work of their youngsters.
- Give validator an incentive to verify earlier work
Validation Group Teams (Hierarchical validation teams)
Validators could should put up a really excessive bond to take part in validation. The quantity of bond wanted is a operate of the goal variety of validators which is a operate of the variety of shards that exists.
However this poses an issue since if there have been the next variety of validators it could be more durable to coordinate a bribe assault on a shard however however Casper can turn out to be inefficient when there are massive variety of validators. A technique this is perhaps solved is to have validators themselves composed of validation teams. The validation group would run in a separate ambient on a separate blockchain from Ethereum.
Within the validation group ambient, work is additional subdivided into smaller chunks. Every particular person validator would get assigned a number of ambients from the shard that validator group was assigned to. This could successfully enable even a small system to take part in validation growing the entire variety of contributors that briber must doubtlessly coordinate with.
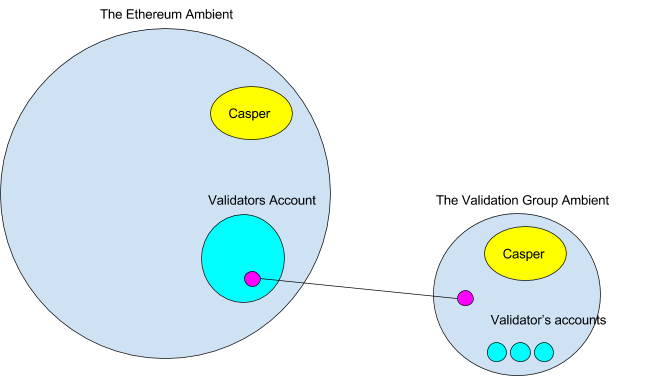
Channels outdoors the Ethereum ambient
To do that the validation group would create a brand new ambient that was related by a channel to the validator group’s ambient. You would possibly marvel how it’s doable to hyperlink to an ambient outdoors of Ethereum. However beneath its easy.
Initially there would solely be a validators account managed by multisig on the Ethereum blockchain. Then the validators would create their very own blockchain (represented as an ambient) which might have the identical system ambients and Casper ambients as Ethereum. After creation, the validator group would join the 2 ambients with a channel. Any message coming into or exiting the ports the should be agreed upon by all of the validators, so the channel must also be protected by a multisig. The code for the multisig would exist within the ports message handler. The channel might solely be adopted by these working each units of ambients. Nodes working simply the Ethereum ambient would see the channel however wouldn’t be capable to comply with it.
This gives a sample that might be elsewhere because it gives a generic approach to join arbitrary ambients to the Ethereum blockchain. These ambients might stand for the state of your private pc or an arbitrary feed of information. Past the examples given right here, there are a lot of different design patterns that make pondering in ambients helpful. Whereas there are nonetheless many lacunae ambients might be a helpful mannequin for computational environments. Ambients provides a brand new dimension to Ethereum’s hypervisor. Fairly actually too. It permits for contract to be much more modular and gives for a handy approach to create administrative domains and mannequin many on a regular basis conditions.
NOTES and PROBLEMS
Listed here are some extra issues to consider.
- SetRoot must fail if the basis didn’t exist within the present namespace. If SetRoot was explicitly used the mum or dad namespace (../<root>) then that tree can be copied to the namespace. If this occurred between shards the tree can be serialized right into a transaction.
- Message
- All messages are assumed to be async. messages can timeout.
- Messages all have a response. The response must be recoded as transaction on requesting shard and the responding shard.
- Blocks would want two components; in transaction and out transactions.
- Seize and delete – The sibling ambient units a price to a path above one other sibling with code for to create an ambient that deletes all of its sub-ambients.
- Answer 1 any motion which may have an effect on a sibling ambient should undergo its message handler
- Answer 2 an ambient might outline a message deal with for all inside message that explicitly disallowed sure sorts of messages.
- Answer 3 reintroduce capabilities as introduced in ambient calculus