Probably the most well-liked subjects within the digital consensus area (a brand new time period for cryptocurrency 2.0 that I’m beta-testing) is the idea of decentralized autonomous entities. There at the moment are a variety of teams quickly getting concerned within the area, together with Bitshares (also referred to as Invictus Improvements) growing “decentralized autonomous firms”, BitAngels’ David Johnston with decentralized purposes, our personal idea of decentralized autonomous firms which has since remodeled into the far more normal and never essentially monetary “decentralized autonomous organizations” (DAOs); all in all, it’s protected to say that “DAOism” is nicely on its strategy to changing into a quasi-cyber-religion. Nevertheless, one of many hidden issues lurking beneath the area is a quite blatant one: nobody even is aware of what all of those invididual phrases imply. What precisely is a decentralized group, what’s the distinction between a corporation and an utility, and what even makes one thing autonomous within the first place? Many people have been annoyed by the shortage of coherent terminology right here; as Bitshares’ Daniel Larimer factors out, “everybody thinks a DAC is only a means of IPOing your centralized firm.” The intent of this text will likely be to delve into a few of these ideas, and see if we are able to give you a minimum of the beginnings of a coherent understanding of what all of this stuff truly are.
Sensible contracts
A sensible contract is the only type of decentralized automation, and is most simply and precisely outlined as follows: a sensible contract is a mechanism involving digital property and two or extra events, the place some or the entire events put property in and property are robotically redistributed amongst these events in accordance with a formulation primarily based on sure information that’s not identified on the time the contract is initiated.
One instance of a sensible contract can be an employment settlement: A needs to pay 500 into the contract, and the funds are locked up. When B finishes the web site, B can ship a message to the contract asking to unlock the funds. If A agrees, the funds are launched. If B decides to not end the web site, B can give up by sending a message to relinquish the funds. If B claims that he completed the web site, however A doesn’t agree, then after a 7-day ready interval it’s as much as choose J to offer a verdict in A or B’s favor.
The important thing property of a sensible contract is straightforward: there’s solely a hard and fast variety of events. The events don’t all should be identified at initialization-time; a promote order, the place A gives to promote 50 items of asset A to anybody who can present 10 items of asset B, can be a sensible contract. Sensible contracts can run on eternally; hedging contracts and escrow contracts are good examples there. Nevertheless, sensible contracts that run on eternally ought to nonetheless have a hard and fast variety of events (eg. a complete decentralized trade is just not a sensible contract), and contracts that aren’t supposed to exist eternally are sensible contracts as a result of present for a finite time essentially implies the involvement of a finite variety of events.
Observe that there’s one grey space right here: contracts that are finite on one facet, however infinite on the opposite facet. For instance, if I need to hedge the worth of my digital property, I’d need to create a contract the place anybody can freely enter and depart. Therefore, the opposite facet of the contract, the events which might be speculating on the asset at 2x leverage, has an unbounded variety of events, however my facet of the contract doesn’t. Right here, I suggest the next divide: if the facet with a bounded variety of events is the facet that intends to obtain a particular service (ie. is a client), then it’s a sensible contract; nevertheless, if the facet with a bounded variety of events is simply in it for revenue (ie. is a producer), then it’s not.
Autonomous Brokers
Autonomous brokers are on the opposite facet of the automation spectrum; in an autonomous agent, there isn’t any needed particular human involvement in any respect; that’s to say, whereas some extent of human effort may be needed to construct the {hardware} that the agent runs on, there isn’t any want for any people to exist which might be conscious of the agent’s existence. One instance of an autonomous agent that already exists in the present day can be a pc virus; the virus survives by replicating itself from machine to machine with out deliberate human motion, and exists virtually as a organic organism. A extra benign entity can be a decentralized self-replicating cloud computing service; such a system would begin off operating an automatic enterprise on one digital personal server, after which as soon as its income enhance it could hire different servers and set up its personal software program on them, including them to its community.
A full autonomous agent, or a full synthetic intelligence, is the dream of science fiction; such an entity would have the ability to modify to arbitrary adjustments in circumstances, and even develop to fabricate the {hardware} wanted for its personal sustainability in idea. Between that, and single function brokers like laptop viruses, is a wide range of prospects, on a scale which may alternatively be described as intelligence or versatility. For instance, the self-replicating cloud service, in its easiest kind, would solely have the ability to hire servers from a particular set of suppliers (eg. Amazon, Microtronix and Namecheap). A extra complicated model, nevertheless, ought to have the ability to determine easy methods to hire a server from any supplier given solely a hyperlink to its web site, after which use any search engine to find new web sites (and, after all, new search engines like google and yahoo in case Google fails). The following stage from there would contain upgrading its personal software program, maybe utilizing evolutionary algorithms, or with the ability to adapt to new paradigms of server rental (eg. make gives for extraordinary customers to put in its software program and earn funds with their desktops), after which the penultimate step consists of with the ability to uncover and enter new industries (the final word step, after all, is generalizing utterly right into a full AI).
Autonomous brokers are a number of the hardest issues to create, as a result of as a way to achieve success they want to have the ability to navigate in an setting that’s not simply sophisticated and quickly altering, but in addition hostile. If a webhosting supplier needs to be unscrupulous, they could particularly find all cases of the service, after which substitute them with nodes that cheat in some trend; an autonomous agent should have the ability to detect such dishonest and take away or a minimum of neutralize dishonest nodes from the system.
Decentralized Functions
A decentralized utility is just like a sensible contract, however totally different in two key methods. Initially, a decentralized utility has an unbounded variety of individuals on all sides of the market. Second, a decentralized utility needn’t be essentially monetary. Due to this second requirement, decentralized purposes are literally a number of the best issues to jot down (or a minimum of, have been the simplest earlier than generalized digital consensus platforms got here alongside). For instance, BitTorrent qualifies as a decentralized utility, as do Popcorn Time, BitMessage, Tor and Maidsafe (notice that Maidsafe can be itself a platform for different decentralized purposes).
Usually, decentralized purposes fall into two lessons, probably with a considerable grey space between the 2. The primary class is a completely nameless decentralized utility. Right here, it doesn’t matter who the nodes are; each participant is actually nameless and the system is made up of a sequence of immediate atomic interactions. BitTorrent and BitMessage are examples of this. The second class is a reputation-based decentralized utility, the place the system (or a minimum of nodes within the system) hold observe of nodes, and nodes keep standing inside the appliance with a mechanism that’s purely maintained for the aim of guaranteeing belief. Standing shouldn’t be transferable or have de-facto financial worth. Maidsafe is an instance of this. In fact, purity is not possible – even a BitTorrent-like system must have friends keep reputation-like statistics of different friends for anti-DDoS functions; nevertheless, the function that these statistics play is solely within the background and really restricted in scope.
An fascinating grey space between decentralized purposes and “one thing else” is purposes like Bitcoin and Namecoin; these differ from conventional purposes as a result of they create ecosystems and there’s a idea of digital property that has worth contained in the context of this ecosystem, in Bitcoin’s case bitcoins and in Namecoin’s case namecoins and domains. As we’ll see beneath, my classification of decentralized autonomous organizations touches on such ideas, and it’s not fairly clear precisely the place they sit.
Decentralized Organizations
Basically, a human group might be outlined as mixture of two issues: a set of property, and a protocol for a set of people, which can or will not be divided into sure lessons with totally different situations for getting into or leaving the set, to work together with one another together with guidelines for below what circumstances the people might use sure components of the property. For instance, think about a easy company operating a sequence of shops. The company has three lessons of members: buyers, workers and prospects. The membership rule for buyers is that of a fixed-size (or optionally quorum-adjustable dimension) slice of digital property; you purchase some digital property to get in, and also you change into an investor till you promote your shares. Workers should be employed by both buyers or different workers particularly licensed by buyers (or different workers licensed by different workers licensed by buyers, and so forth recursively) to take part, and may also be fired in the identical means, and prospects are an open-membership system the place anybody can freely work together with the shop within the apparent formally sanctioned means for any time. Suppliers, on this mannequin, are equal to workers. A nonprofit charity has a considerably totally different construction, involving donors and members (charity recipients might or will not be thought-about members; the choice view sees the optimistic increments within the recipients’ welfare as being the charity’s “product”).
The concept of a decentralized group takes the identical idea of a corporation, and decentralizes it. As an alternative of a hierarchical construction managed by a set of people interacting in particular person and controlling property by way of the authorized system, a decentralized group includes a set of people interacting with one another in accordance with a protocol laid out in code, and enforced on the blockchain. A DO might or might not make use of the authorized system for some safety of its bodily property, however even there such utilization is secondary. For instance, one can take the shareholder-owned company above, and transplant it completely on the blockchain; a long-running blockchain-based contract maintains a document of every particular person’s holdings of their shares, and on-blockchain voting would permit the shareholders to pick the positions of the board of administrators and the staff. Sensible property programs may also be built-in into the blockchain instantly, doubtlessly permitting DOs to manage autos, security deposit packing containers and buildings.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations
Right here, we get into what is probably the holy grail, the factor that has the murkiest definition of all: decentralized autonomous organizations, and their company subclass, decentralized autonomous firms (or, extra lately, “firms”). The perfect of a decentralized autonomous group is straightforward to explain: it’s an entity that lives on the web and exists autonomously, but in addition closely depends on hiring people to carry out sure duties that the automaton itself can’t do.
Given the above, the essential a part of the definition is definitely to give attention to what a DAO is just not, and what’s not a DAO and is as an alternative both a DO, a DA or an automatic agent/AI. Initially, let’s think about DAs. The primary distinction between a DA and a DAO is {that a} DAO has inner capital; that’s, a DAO comprises some sort of inner property that’s precious ultimately, and it has the power to make use of that property as a mechanism for rewarding sure actions. BitTorrent has no inner property, and Bitcloud/Maidsafe-like programs have popularity however that popularity is just not a saleable asset. Bitcoin and Namecoin, then again, do. Nevertheless, plain previous DOs even have inner capital, as do autonomous brokers.
Second, we are able to take a look at DOs. The plain distinction between a DO and a DAO, and the one inherent within the language, is the phrase “autonomous”; that’s, in a DO the people are those making the choices, and a DAO is one thing that, in some trend, makes choices for itself. It is a surprisingly difficult distinction to outline as a result of, as dictatorships are all the time eager to level out, there’s actually no distinction between a sure set of actors making choices instantly and that set of actors controlling the entire data by way of which choices are made. In Bitcoin, a 51% assault between a small variety of mining swimming pools could make the blockchain reverse transactions, and in a hypothetical decentralized autonomous company the suppliers of the information inputs can all collude to make the DAC suppose that sending all of its cash to1FxkfJQLJTXpW6QmxGT6oF43ZH959ns8Cq constitutes paying for one million nodes’ price of computing energy for ten years. Nevertheless, there’s clearly a significant distinction between the 2, and so we do have to outline it.
My very own effort at defining the distinction is as follows. DOs and DAOs are each weak to collusion assaults, the place (in the very best case) a majority or (in worse instances) a major share of a sure kind of members collude to particularly direct the D*O’s exercise. Nevertheless, the distinction is that this: in a DAO collusion assaults are handled as a bug, whereas in a DO they’re a function. In a democracy, for instance, the entire level is {that a} plurality of members select what they like finest and that answer will get executed; in Bitcoin’s then again, the “default” habits that occurs when everybody acts in accordance with particular person curiosity with none need for a particular consequence is the intent, and a 51% assault to favor a particular blockchain is an aberration. This enchantment to social consensus is just like the definition of a authorities: if a neighborhood gang begins charging a property tax to all shopowners, it might even get away with it in sure components of the world, however no significant slice of the inhabitants will deal with it as respectable, whereas if a authorities begins doing the identical the general public response will likely be tilted within the different course.
Bitcoin is an fascinating case right here. Basically, it appears to be a lot nearer to a DAO than a DO. Nevertheless, there was one incident in 2013 the place the fact proved to be quite totally different. What occurred was that an distinctive block was (a minimum of we hope) by chance produced, which was handled as legitimate in accordance with the BitcoinQt 0.8 purchasers, however invalid in accordance with the foundations of BitcoinQt 0.7. The blockchain forked, with some nodes following the blockchain after this distinctive block (we’ll name this chain B1), and the opposite nodes that noticed that block as invalid engaged on a separate blockchain (which we’ll name B2). Most mining swimming pools had upgraded to BitcoinQt 0.8, in order that they adopted B1, however most customers have been nonetheless on 0.7 and so adopted B2. The mining pool operators got here collectively on IRC chat, and agreed to change their swimming pools to mining on B2, since that consequence can be easier for customers as a result of it could not require them to improve, and after six hours the B2 chain overtook B1 on account of this deliberate motion, and B1 fell away. Thus, on this case, there was a deliberate 51% assault which was seen by the group as respectable, making Bitcoin a DO quite than a DAO. Normally, nevertheless, this doesn’t occur, so one of the simplest ways to categorise Bitcoin can be as a DAO with an imperfection in its implementation of autonomy.
Nevertheless, others will not be content material to categorise Bitcoin as a DAO, as a result of it’s not actually sensible sufficient. Bitcoin doesn’t suppose, it doesn’t exit and “rent” individuals apart from the mining protocol, and it follows easy guidelines the upgrading course of for which is extra DO-like than DAO-like. Folks with this view would see a DAO as one thing that has a big diploma of autonomous intelligence of its personal. Nevertheless, the difficulty with this view is that there have to be a distinction made between a DAO and an AA/AI. The excellence right here is arguably this: an AI is totally autonomous, whereas a DAO nonetheless requires heavy involvement from people particularly interacting in accordance with a protocol outlined by the DAO as a way to function. We will classify DAOs, DOs (and plain previous Os), AIs and a fourth class, plain previous robots, in accordance with previous quadrant chart, with one other quadrant chart to categorise entities that do not need inner capital thus altogether making a dice:
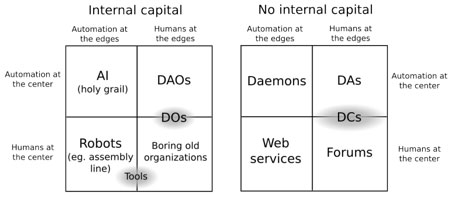
DAOs == automation on the heart, people on the edges. Thus, on the entire, it makes most sense to see Bitcoin and Namecoin as DAOs, albeit ones that hardly cross the brink from the DA mark. The opposite essential distinction is inner capital; a DAO with out inner capital is a DA and a corporation with out inner capital is a discussion board; the G8, for instance, would qualify as a discussion board. DCs within the graph above are “decentralized communities”; an instance of that may be one thing like a decentralized Reddit, the place there’s a decentralized platform, however there’s additionally a group round that platform, and it’s considerably ambiguous whether or not the group or the protocol is really “in cost”.
Decentralized Autonomous Companies
Decentralized autonomous firms/firms are a smaller matter, as a result of they’re principally a subclass of DAOs, however they’re price mentioning. For the reason that primary exponent of DAC as terminology is Daniel Larimer, we are going to borrow as a definition the purpose that he himself constantly promotes: a DAC pays dividends. That’s, there’s a idea of shares in a DAC that are purchaseable and tradeable in some trend, and people shares doubtlessly entitle their holders to continuous receipts primarily based on the DAC’s success. A DAO is non-profit; although you can also make cash in a DAO, the best way to do this is by collaborating in its ecosystem and never by offering funding into the DAO itself. Clearly, this distinction is a murky one; all DAOs comprise inner capital that may be owned, and the worth of that inner capital can simply go up because the DAO turns into extra highly effective/well-liked, so a big portion of DAOs are inevitably going to be DAC-like to some extent.
Thus, the excellence is extra of a fluid one and hinges on emphasis: to what extent are dividends the primary level, and to what extent is it about incomes tokens by participation? Additionally, to what extent does the idea of a “share” exist versus easy digital property? For instance, a membership on a nonprofit board is just not actually a share, as a result of membership steadily will get granted and confiscated at will, one thing which might be unacceptable for one thing categorized as investable property, and a bitcoin is just not a share as a result of a bitcoin doesn’t entitle you to any declare on income or decision-making capability contained in the system, whereas a share in an organization positively is a share. In the long run, maybe the excellence would possibly in the end be the surprisingly obscure level of whether or not or not the revenue mechanism and the consensus mechanism are the identical factor.
The above definitions are nonetheless not shut to finish; there’ll probably be grey areas and holes in them, and precisely what sort of automation a DO will need to have earlier than it turns into a DAO is a really exhausting query to reply. Moreover, there’s additionally the query of how all of this stuff must be constructed. An AI, for instance, ought to probably exist as a community of personal servers, every one operating usually proprietary native code, whereas a DO must be absolutely open supply and blockchain-based. Between these two extremes, there’s numerous totally different paradigms to pursue. How a lot of the intelligence must be within the core code? Ought to genetic algorithms be used for updating code, or ought to or not it’s futarchy or some voting or vetting mechanism primarily based on people? Ought to membership be corporate-style, with sellable and transferable shares, or nonprofit-style, the place members can vote different members out and in? Ought to blockchains be proof of labor, proof of stake, or reputation-based? Ought to DAOs attempt to keep balances in different currencies, or ought to they solely reward habits by issuing their very own inner token? These are all exhausting issues and we have now solely simply begun scratching the floor of them.

